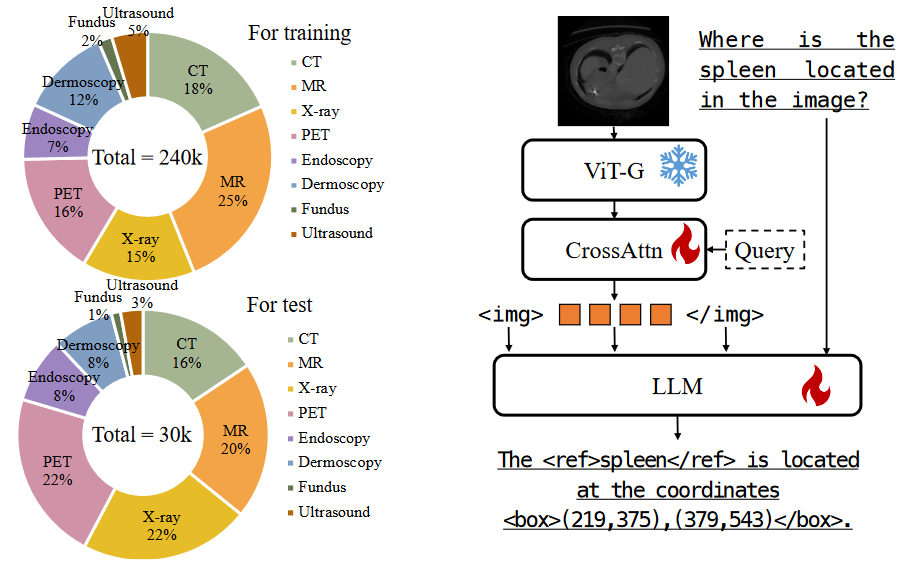
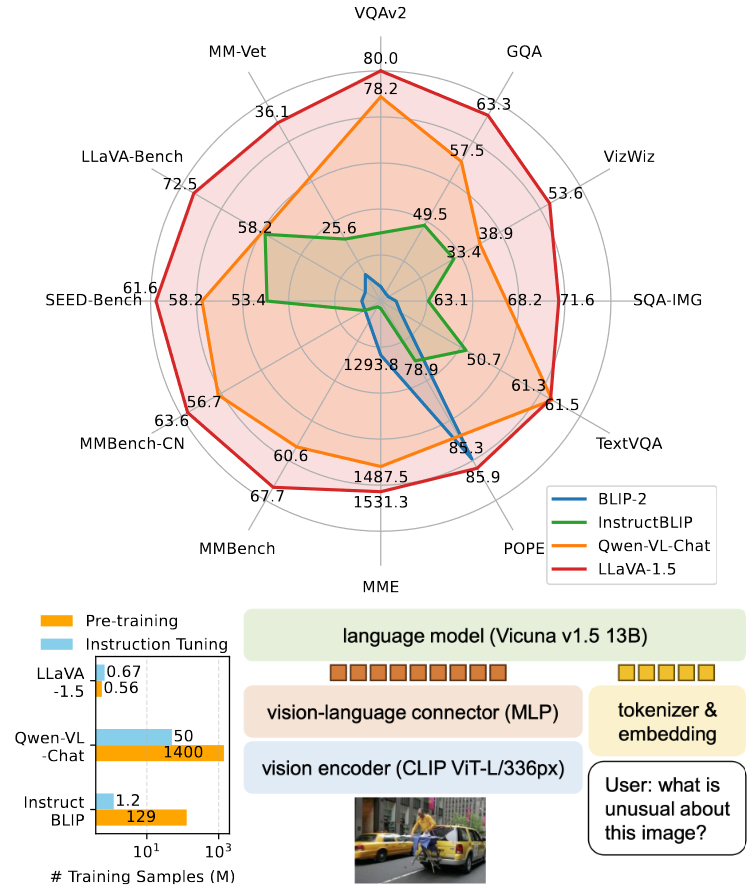
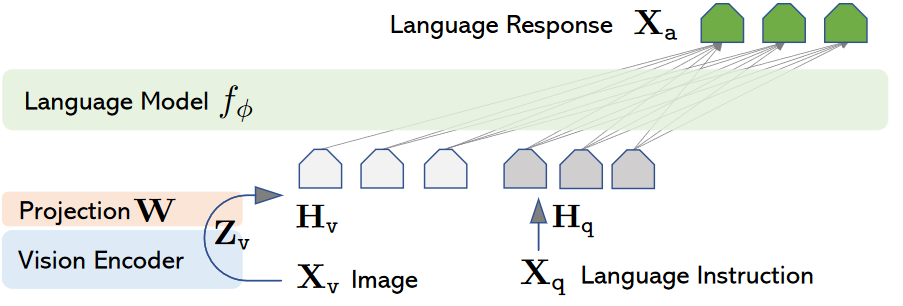
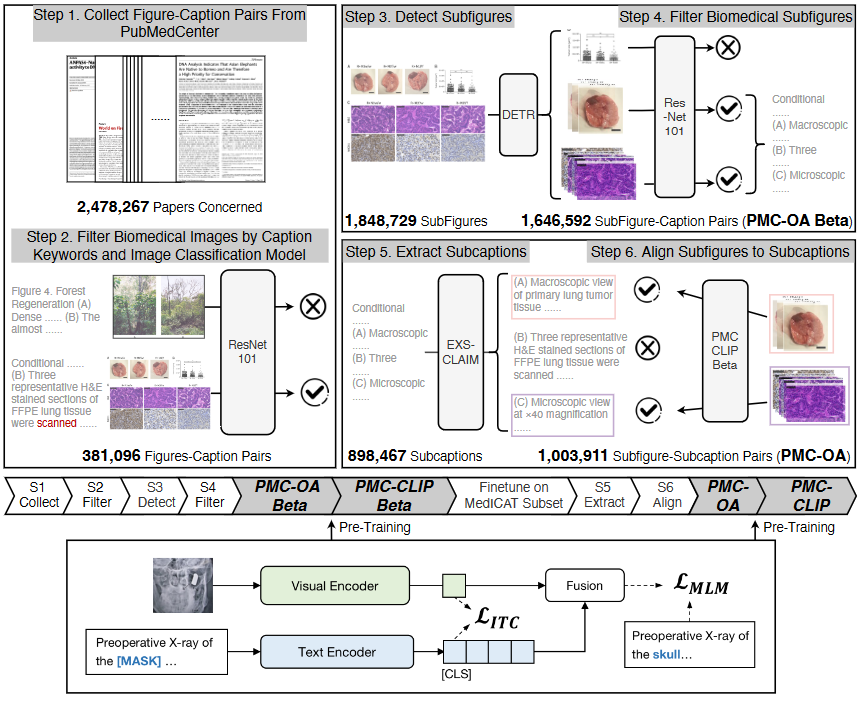
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Animator:
"""在动画中绘制数据"""
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None,
ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1,
figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes, ]
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(
self.axes[0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
|